What is PoE (Power over Ethernet) and PoC (Power over Cable)?
Power-over Ethernet (PoE), Power-over-Cable (PoC) and now Power-over-HDBaseT (PoH) are all based on the same basic principle of simultaneously providing both data signal and power from one device to another over the same cable. HowToAV takes a look at how each one differs and the benefits of PoE powered devices.
What is Power-over-Ethernet?
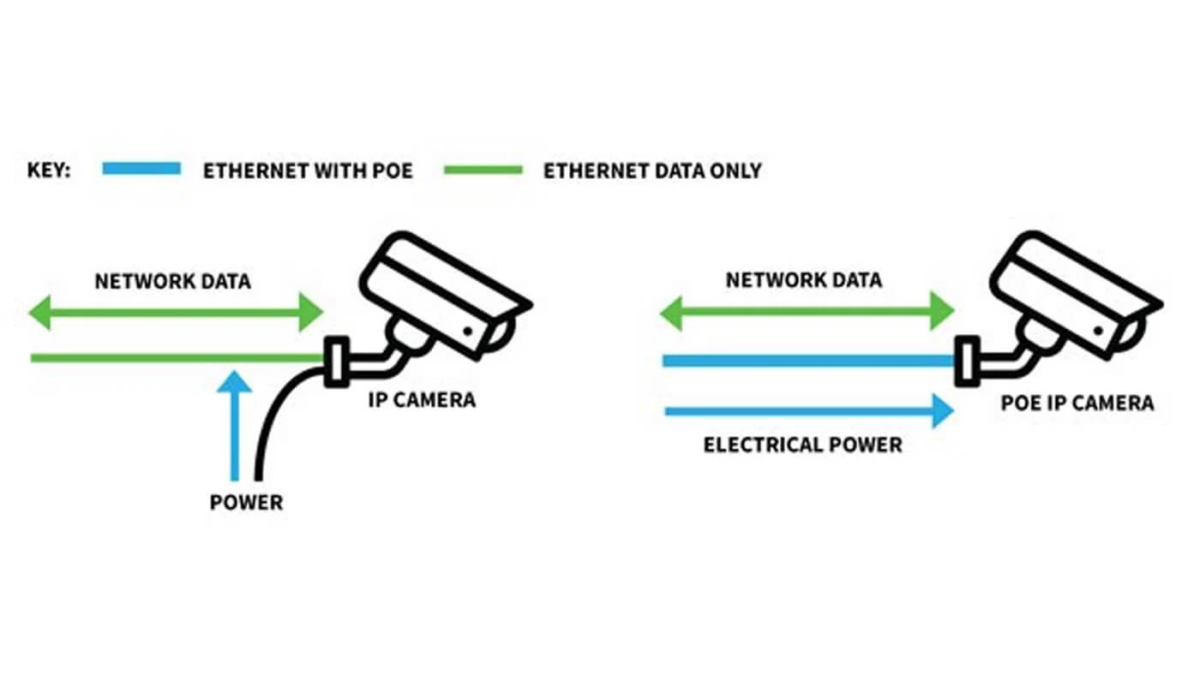
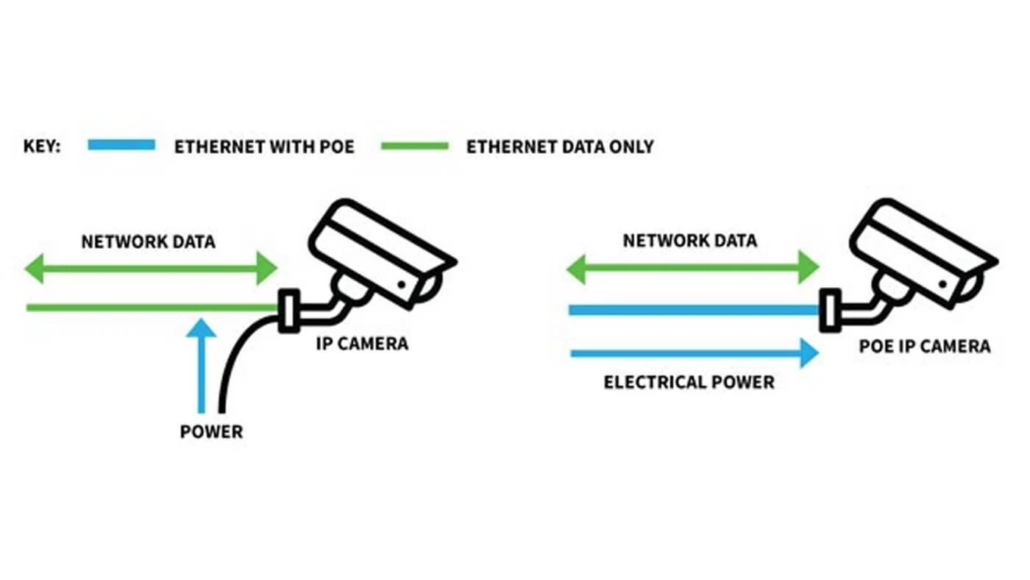
Power-over-Ethernet (often referred to as PoE) is a technology which provides electrical power over standard Ethernet cables – in most cases providing the power delivery simultaneously with the data signals sent from one device to another. As an example, a CCTV camera would normally require both data cable and an external power supply – from two separate cables. However, a PoE enabled camera will receive both data and power over the same network cable from a network / PoE switch or from the system’s NVR.
What is the difference between Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) and Power-over-Cable (PoC)?
PoE (Power-over-Ethernet) is an electrical industry standard which allows electrical power to be transmitted simultaneously with data signals over Cat5e/6/7 cable. PoE is standardised to adhere to specific voltage ranges between 37 and 57 volts. This ensures that any PoE device connected to a system receives a compatible power supply. Power over Ethernet will only apply power to the line once a remote device / receiver has been detected on the line.
PoC* (Power-over-Cable) works to similar principles (supplying simultaneous power and data signals over Cat cable) but is non-standardised and is applied to proprietary systems. Therefore, the voltage supply can be set to meet the needs of a specific product/system (which may be lower or higher than voltage range of PoE). Power over Cable will apply power to the line directly without detecting a device at the remote/receiver end.
*(PoC also sometimes refers to Power-over-Coaxial cable)
PoH (Power-over-HDBaseT) – the latest Video-over-IP technology – HDBaseT – simultaneously transmits HD video, audio, control signals and power from device to device over Ethernet cable to distances of up to 100 metres.
Phantom Power – not usually considered within the PoE / PoC ‘family’, but Phantom Power sends a 12-48 volt DC voltage along with the audio signal form an amplifier for use with condenser microphones.
What are the benefits of using PoE?

PoE has many benefits to an installation:
- Saves time – by not having to have electrical power cabling installed and not needing a qualified electrician to fit network cables, a person simply finds the right location for the device, installs the device, and adds to the network via an Ethernet connection, saving both time and installation costs.
- Flexible – as it does not have to be attached to an electrical outlet, devices such as CCTV devices and wireless access points can be placed wherever they are needed most, and easily repositioned anytime if required.
- Safe – Power over Ethernet usually uses 48V DC, which is classified as a safe voltage by the UL Standards. PoE also has built-in safety features, such as if there is an interruption in the connection, the PSE automatically stops sending power, and starts a handshaking process before sending power again. Meaning if there is damage to a cable, for example fraying, the power is stopped.
- Reliable – PoE power comes from a central and compatible source, rather than a collection of distributed wall adapters. It can be backed-up by an uninterruptible power supply or controlled to easily disable or reset devices.
- Scalable – as it has power available on the network, this means that installation and distribution of network connections is simple and effective.
What devices use PoE?
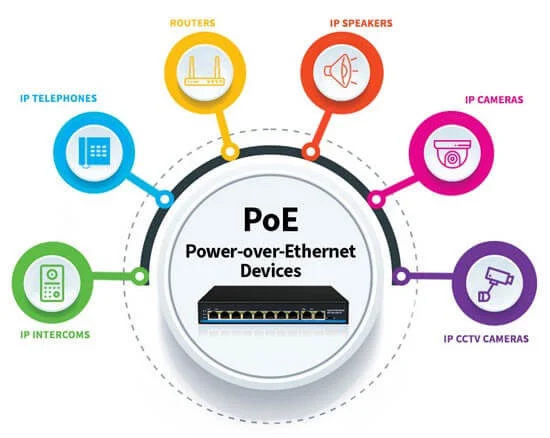
As technology moves us further and further into the internet of things (smart devices and IP connectivity), the range of products and equipment that is powered via PoE continues to increase. For example, PoE devices include:
- IP Telephones – Voice-over-IP (VoIP) phones are connected via a single network cable, taking both data and power from the network switch
- IP CCTV cameras – IP cameras are now the industry standard throughout the world, ensuring fast, easy installation, set-up and control and small to large scale security systems
- IP Intercoms – Door Intercom systems are in effect ‘armored telephones’ and therefore work in the same way, transmitting data (video, sound and control) and power signals over the same network cable
- IP Speakers – Audio-over-IP is the latest generation of professional distributed sound systems for music and public address, where the entire audio system is connected via LAN / WAN networks. This allows the IP speakers to be connected via a single (Ethernet) cable including PoE
- IP Access Control – Bluetooth, RFID and biometric access control points similarly are connected over a network, transmitting simultaneous data and power over the same single cable
What are the benefits of using PoE / PoC?
- Time and labor costs are reduced – Power over Cable is great for when you have an existing analogue system as you can use the old system cables already installed and add to it.
- More project opportunities – As Power over Ethernet is not recommended for sending network signals over long distances, PoC becomes a great solution as it has longer transmission distances up to 400m.
- Safe – like PoE technology, PoC has built-in safety features such as emergency power supply cut off.
Source: https://cie-group.com/how-to-av/videos-and-blogs/difference-between-poe-and-poc